The Killer Glossary
draft
How do we know? NASA's FAQs - Audio Introduction to Killer Oceans
Think Globally - - Act Locally
Latiude -
How do we know? NASA's FAQs - Audio Introduction to Killer Oceans
Think Globally - - Act Locally

Adiabatic, an adjective used to tell a condition or something relating a process where heat remains in a system. "An adiabatic compression of perfect gases."
Abrupt climate changes - "An abrupt climate change is a sudden and significant shift in some aspect of the climate." Example, sitting in a canoe, you lean too far to retrieve a dropped oar; you pass a critical threshold and the canoe flips over. You are now in the river unable to right your canoe.
Albedo- From the Latin word for whiteness. Albedco serves to reflect sunlight back into space. Warming land surfaces (agriculture, deforestation) and ocean warming create feed-back loops leading to increased ice and snow melt.
Anthropocene - The geological period of human dominance of Earth's climate and environment.
Celsius -
Faherenheit
Periapsis - Nearest and farthest points in a planetary body's orbit.
Global Ocean Warming - Direct solar energy and atmospheric heat mix easily with ocean's top layer (600 feet); the lower 95 percent warms slow in human terms. The lower layer takes about 3,000 years to mix and come to equilibrium with the top layer and atmospehre. Dessler - - See Other Climate Investigations
Killer Oeans - Five oceans undergoing physical and chemical changes more rapidly than life can adapt. Human greenhouse gas emissions produce rapid ocean warming and rapid acidification; plastic pollution poisons, sea life, including Arctic plankton. Only within a human context do Earth's oceans become "killer oceans," during the anthropocene..
lag time - A period of time between greenhouse gas emissions and planet warming. Greenhouse effect lags behind CO2 emissions, for example; hence, today greenhouse gas emissions are "in the pipeline" and inevitable for centuries, also known as committed warming.
Obliquity - Neither a right angle nor parallel
Milankovitch cycles, Milutin Milankovitch - Serbian mathemtician credited for to discover the role of Earth's orbit and growth of the ice-ages.
Moraine (debris): Four types of moraines:: lateral moraines, medial moraines, supraglacial moraines, and terminal moraines. Lateral moraines form next to glaciers, alongside. Till consisting of a mixture of clay, sand, pebbles and boulders form from grinding movements of glaciers. Resulting sediments from moraines give evidence of glacier growth and retreat.
Perihelion - The nearest point to the Sun in a planet's movement around the Sun.
Radiative Forcing (climate forcing) - The most important climate science idea. The difference between energy absorbed by the earth and energy ratiated back into space. Radiative " forcing is defined as the response to an instantaneous change, before the temperature of the planet has adjusted to the change."
Younger Dryas -
Subarial - Existing on Earth's surface, not below ground, under water.
Dessler, Andrew E.. Introduction to Modern Climate Change (p. 93). Cambridge University Press. Kindle Edition.
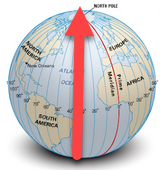
 In Humboldt's geography, latitude shows a geographic coordinate. Such coordinates tell north–south positions of a point on the Earth's surface. An angle, 90° (North or South) at the poles and 0° at the equator. Latitude Lines run parallel, east to west. We see latitude lines as circles between Earth's poles.
In Humboldt's geography, latitude shows a geographic coordinate. Such coordinates tell north–south positions of a point on the Earth's surface. An angle, 90° (North or South) at the poles and 0° at the equator. Latitude Lines run parallel, east to west. We see latitude lines as circles between Earth's poles.
Yes, this is a metaphore. Sometimes when talking about science it helps to use metaphores and other figures of speech.
A human generation is about 27 years, according to some sociologists. So figure that 200 years in the future will be the time of the 7th Generation. For our purpposes, from now until the time of the 7th Generatin, Earth will neither have returned to its pre-industrial temperatures nor will the polar albedo have returned.